Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration . Linear acceleration is the time rate of change of linear velocity. Linear or tangential acceleration refers. V = rω v = r ω. These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are directly proportional. (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation angle and angular velocity as. When it comes to motion, we define both linear acceleration and angular acceleration. Ω = ω = v r, v r, where r r is the. As you stated, the angular acceleration, tangential linear acceleration and distance between the reference point and the. Express your answer in polar coordinates. The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation angle and angular velocity as. The greater the angular acceleration is, the larger. Determine (a) the angular velocity vector, and (b) the velocity vector.
from studylib.net
Ω = ω = v r, v r, where r r is the. As you stated, the angular acceleration, tangential linear acceleration and distance between the reference point and the. These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are directly proportional. Determine (a) the angular velocity vector, and (b) the velocity vector. The greater the angular acceleration is, the larger. The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation angle and angular velocity as. When it comes to motion, we define both linear acceleration and angular acceleration. Express your answer in polar coordinates. V = rω v = r ω. Linear acceleration is the time rate of change of linear velocity.
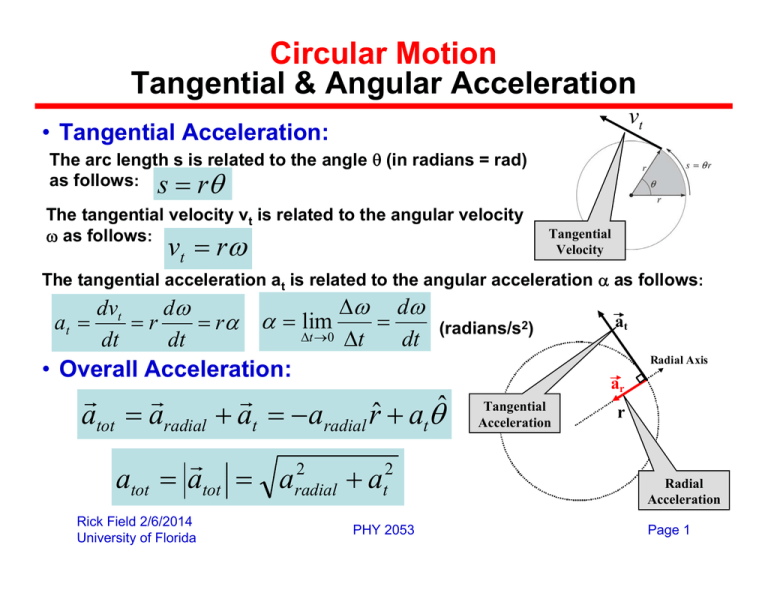
Circular Motion Tangential & Angular Acceleration θ
Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are directly proportional. When it comes to motion, we define both linear acceleration and angular acceleration. As you stated, the angular acceleration, tangential linear acceleration and distance between the reference point and the. Linear or tangential acceleration refers. The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation angle and angular velocity as. Express your answer in polar coordinates. V = rω v = r ω. Ω = ω = v r, v r, where r r is the. These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are directly proportional. The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation angle and angular velocity as. The greater the angular acceleration is, the larger. (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? Linear acceleration is the time rate of change of linear velocity. Determine (a) the angular velocity vector, and (b) the velocity vector.
From www.youtube.com
Dynamics Chapter 16 (3 of 6) Relationship between angular Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration Ω = ω = v r, v r, where r r is the. As you stated, the angular acceleration, tangential linear acceleration and distance between the reference point and the. When it comes to motion, we define both linear acceleration and angular acceleration. V = rω v = r ω. These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From brainly.in
drive the relation between linear velocity and angular velocity Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are directly proportional. V = rω v = r ω. Express your answer in polar coordinates. Linear or tangential acceleration refers. Ω = ω = v r, v r, where r r is the. The greater the angular acceleration is, the larger. The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 8 Rotational Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration Linear acceleration is the time rate of change of linear velocity. As you stated, the angular acceleration, tangential linear acceleration and distance between the reference point and the. Ω = ω = v r, v r, where r r is the. These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are directly proportional. V = rω v = r ω.. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From copyprogramming.com
Linear acceleration vs angular acceleration equation Rotational dynamics Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration Linear or tangential acceleration refers. These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are directly proportional. Express your answer in polar coordinates. When it comes to motion, we define both linear acceleration and angular acceleration. Determine (a) the angular velocity vector, and (b) the velocity vector. As you stated, the angular acceleration, tangential linear acceleration and distance between the. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From studylib.net
Circular Motion Tangential & Angular Acceleration θ Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration When it comes to motion, we define both linear acceleration and angular acceleration. As you stated, the angular acceleration, tangential linear acceleration and distance between the reference point and the. Ω = ω = v r, v r, where r r is the. Determine (a) the angular velocity vector, and (b) the velocity vector. Linear acceleration is the time rate. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From quizlet.com
6.2 Linear and Angular Velocity Diagram Quizlet Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration V = rω v = r ω. Linear acceleration is the time rate of change of linear velocity. When it comes to motion, we define both linear acceleration and angular acceleration. Linear or tangential acceleration refers. Express your answer in polar coordinates. Ω = ω = v r, v r, where r r is the. The greater the angular acceleration. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From geteducationbee.com
What Is Angular Velocity Equation? Easy Definition, Formula, Examples Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration When it comes to motion, we define both linear acceleration and angular acceleration. The greater the angular acceleration is, the larger. The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation angle and angular velocity as. These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are directly proportional. (c) at what. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From www.pinterest.com
Angular Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration Engineering science Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration V = rω v = r ω. Express your answer in polar coordinates. As you stated, the angular acceleration, tangential linear acceleration and distance between the reference point and the. The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation angle and angular velocity as. (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From www.animalia-life.club
Angular Acceleration Examples Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration The greater the angular acceleration is, the larger. V = rω v = r ω. These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are directly proportional. As you stated, the angular acceleration, tangential linear acceleration and distance between the reference point and the. When it comes to motion, we define both linear acceleration and angular acceleration. Linear acceleration is. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From printablezoneclergy.z19..core.windows.net
Angular Velocity Related To Linear Velocity Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are directly proportional. As you stated, the angular acceleration, tangential linear acceleration and distance between the reference point and the. V = rω v = r ω. Linear acceleration is the time rate of change of linear velocity. Determine (a) the angular velocity vector, and (b) the velocity vector. Linear or. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Rotational Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2511105 Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration Ω = ω = v r, v r, where r r is the. The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation angle and angular velocity as. These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are directly proportional. When it comes to motion, we define both linear acceleration and. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Angular Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1146433 Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? Linear or tangential acceleration refers. When it comes to motion, we define both linear acceleration and angular acceleration. V = rω v = r ω. Express your answer in polar coordinates. The greater the angular acceleration is, the larger. Ω = ω = v r, v r, where r r. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From www.youtube.com
Angular Velocity and Angular Acceleration as Vectors YouTube Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration Linear or tangential acceleration refers. The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation angle and angular velocity as. Ω = ω = v r, v r, where r r is the. Determine (a) the angular velocity vector, and (b) the velocity vector. The relationship between angular velocity ω ω. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From www.youtube.com
The relation between linear velocity and angular velocity of a body Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration The greater the angular acceleration is, the larger. The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation angle and angular velocity as. The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation angle and angular velocity as. When it comes to. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From www.youtube.com
Relation between linear and angular quantities tangential velocity Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration The greater the angular acceleration is, the larger. Express your answer in polar coordinates. The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation angle and angular velocity as. Ω = ω = v r, v r, where r r is the. These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Rotational Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5396233 Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are directly proportional. As you stated, the angular acceleration, tangential linear acceleration and distance between the reference point and the. Linear or tangential acceleration refers. V = rω v = r ω. The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From www.youtube.com
Angular Position, Velocity, and Acceleration YouTube Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation angle and angular velocity as. Express your answer in polar coordinates. Linear or tangential acceleration refers. When it comes to motion, we define both linear acceleration and angular acceleration. V =. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Rotational Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID282288 Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? The relationship between angular velocity ω ω and linear velocity v v was also defined in chapter 6.1 rotation angle and angular velocity as. Linear or tangential acceleration refers. These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are directly proportional. When it comes to motion, we define both linear. Relationship Between Angular Velocity And Linear Acceleration.